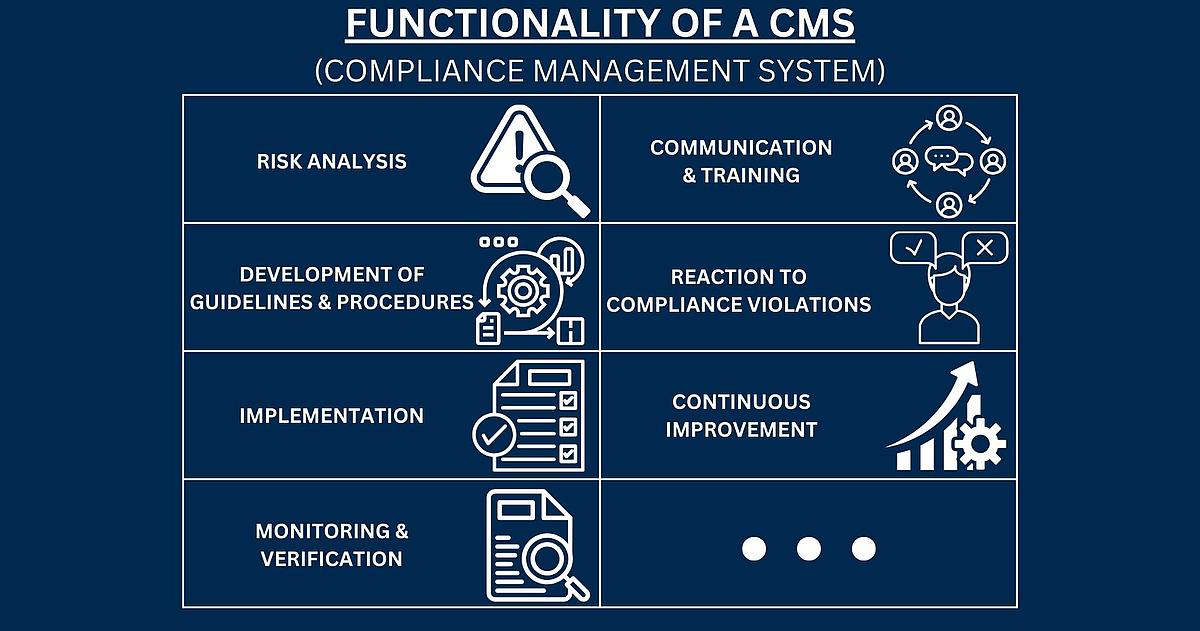
1. Detection of the Violation
Compliance violations are often discovered through internal controls, audits or information from employees (whistleblowing). In some cases, external parties such as regulatory authorities or customers may also report violations.
2. Investigation
Once a potential violation has been identified, the company typically conducts an internal investigation to clarify the facts. This investigation is usually conducted by the compliance department, possibly in cooperation with the legal department. The aim is to understand the nature of the violation, identify the individuals involved, and determine the extent of the damage.
3. Disciplinary Measures
If the breach is confirmed, the company may take disciplinary action against the employees involved. These may range from warnings to fines to termination, depending on the severity of the violation and the company's internal policies.
4. Reporting to Supervisory Authorities
In many cases, especially if legal regulations have been violated, the company is obliged to report the violation to the relevant supervisory authorities. This may lead to further investigations by external authorities.