Rate of Return Definition: What is Rate of Return
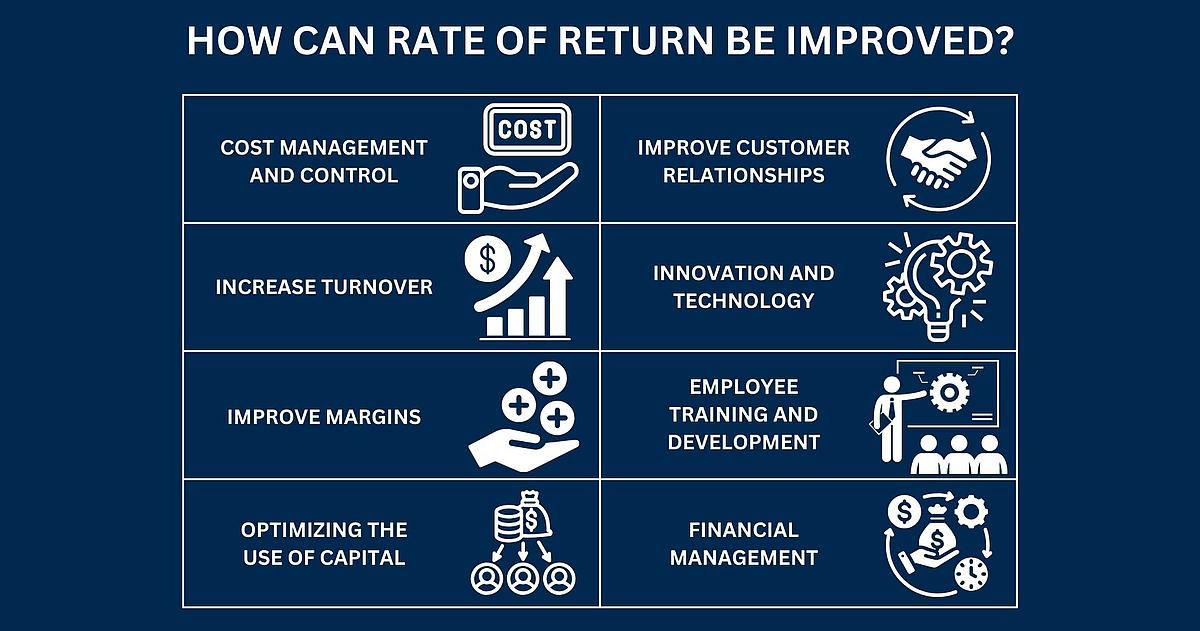
Rate of Return is an economic measure that represents the efficiency of a company in generating profits in relation to the resources used. It shows how well a company uses its investments to generate profits. Rate of Return is often expressed as a percentage and helps to evaluate a company's financial performance and competitiveness. There are different forms of Rate of Return, including Return on Equity, Return on Assets and Return on Sales, each of which highlights different aspects of a company's performance.